Introduction to Conversational AI
Explore the fundamentals of chatbots and voice assistants, the evolution of conversational interfaces, and key use cases across industries.
Learning Objectives
- Understand what conversational AI is and its key components
- Trace the evolution of conversational interfaces from early chatbots to modern AI assistants
- Identify the business value and use cases for conversational AI across different industries
- Recognize the differences between rule-based and AI-powered conversational systems
- Understand the basic architecture of a conversational AI system
What is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI refers to technologies that enable computers to understand, process, and respond to human language in a natural and meaningful way. These systems combine natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and other AI techniques to create interfaces that allow humans to interact with computers using everyday language rather than specialized commands or graphical interfaces.
At its core, conversational AI aims to make human-computer interaction more intuitive by mimicking human conversation. This includes understanding not just the literal words being spoken or typed, but also the intent behind them, the context in which they occur, and the appropriate way to respond.
Key Components of Conversational AI
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
The ability to comprehend human language input, extract meaning, identify intents, and recognize entities.
Natural Language Generation (NLG)
The ability to formulate appropriate, contextually relevant responses in natural language.
Dialog Management
The system that maintains conversation state, manages context, and determines appropriate next steps in a conversation.
Integration Layer
Components that connect the conversational interface to backend systems, databases, APIs, and business logic.
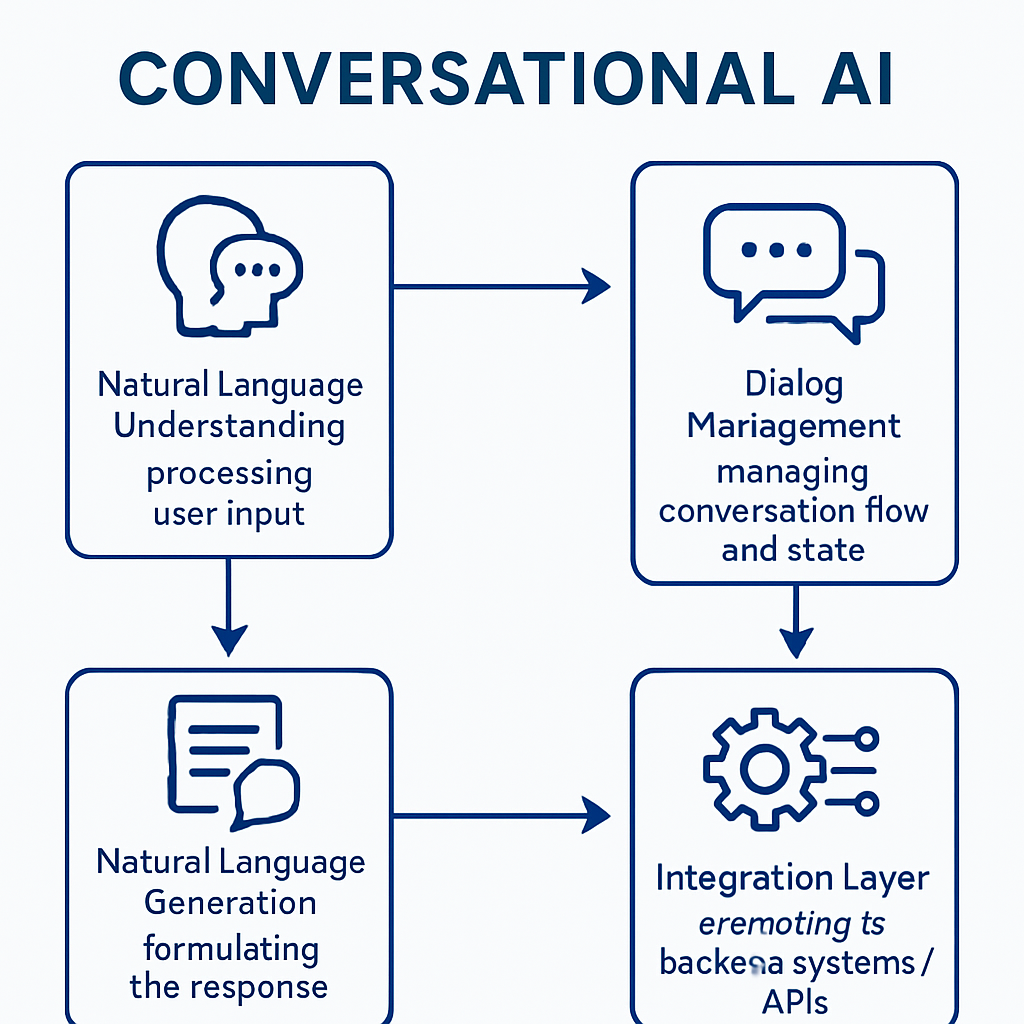
Figure 1: Key Components of a Conversational AI System
Evolution of Conversational Interfaces
The journey of conversational interfaces spans several decades, evolving from simple rule-based systems to sophisticated AI-powered assistants capable of understanding nuance and context.
Early Chatbots (1960s-1990s)
The earliest conversational systems were rule-based programs designed to mimic human conversation through pattern matching and predefined responses. ELIZA, created by Joseph Weizenbaum in 1966, is often considered the first chatbot. It simulated a psychotherapist by recognizing keywords and responding with pre-programmed phrases, creating an illusion of understanding.
These early systems relied on simple pattern-matching techniques and lacked true language understanding. They followed rigid scripts and could not adapt to unexpected inputs or learn from interactions.
Statistical NLP Systems (2000s-2010s)
The next generation of conversational systems incorporated statistical natural language processing techniques. These systems used machine learning algorithms trained on large datasets to recognize patterns in language and make probabilistic decisions about meaning and appropriate responses.
This era saw the emergence of virtual assistants like Apple's Siri (2011), Google Now (2012), Microsoft's Cortana (2014), and Amazon's Alexa (2014). These systems could perform specific tasks like setting alarms, answering factual questions, or controlling smart home devices, but still struggled with complex queries, context switching, and natural conversation flow.
Modern AI-Powered Conversational Systems (2015-Present)
The current generation of conversational AI systems leverages deep learning, particularly transformer-based models like BERT and GPT, to achieve unprecedented levels of language understanding and generation. These systems can:
- Understand context and maintain coherence across multiple turns in a conversation
- Recognize entities, relationships, and user intents with high accuracy
- Generate natural-sounding responses that adapt to the conversation context
- Learn from interactions to improve over time
- Handle ambiguity and understand implied meaning
Modern conversational AI systems like ChatGPT, Google's LaMDA, and Amazon Lex combine these advanced language models with specialized components for task completion, knowledge retrieval, and integration with external systems.
Conversation Simulator
Try interacting with different types of conversational systemsBusiness Value and Use Cases
Conversational AI delivers significant business value across various industries by enhancing customer experience, increasing operational efficiency, and enabling new service models.
Customer Service and Support
Conversational AI can handle routine customer inquiries, troubleshoot common problems, and escalate complex issues to human agents when necessary. This reduces wait times, enables 24/7 support, and allows human agents to focus on high-value interactions.
Example: Banking chatbots that can check account balances, process transfers, report lost cards, and answer frequently asked questions about banking services.
Sales and Marketing
Conversational interfaces can guide customers through the buying journey, recommend products, answer product questions, and facilitate transactions.
Example: E-commerce chatbots that help customers find products, compare options, check availability, and complete purchases.
Healthcare
In healthcare, conversational AI can assist with appointment scheduling, medication reminders, symptom checking, and providing health information.
Example: Virtual health assistants that conduct initial symptom assessments, provide medication reminders, and offer mental health support through guided conversations.
Human Resources
HR departments use conversational AI to streamline employee onboarding, answer policy questions, facilitate leave requests, and provide information about benefits.
Example: HR bots that help employees find information about company policies, submit time-off requests, and navigate benefits enrollment.
